Why blockchain interoperability matters
Blockchain interoperability sounds scary, but the idea is simple: different blockchains should talk to each other as easily as websites talk over the internet. Right now, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana and others are like isolated islands with their own rules and assets. Interoperability protocols build “ferries and airports” between these islands, letting data and value move safely. This is crucial both for regular users and for companies choosing blockchain interoperability platforms for enterprises, because nobody wants to be locked forever into a single chain that might become outdated or too expensive.
Key concepts in plain language
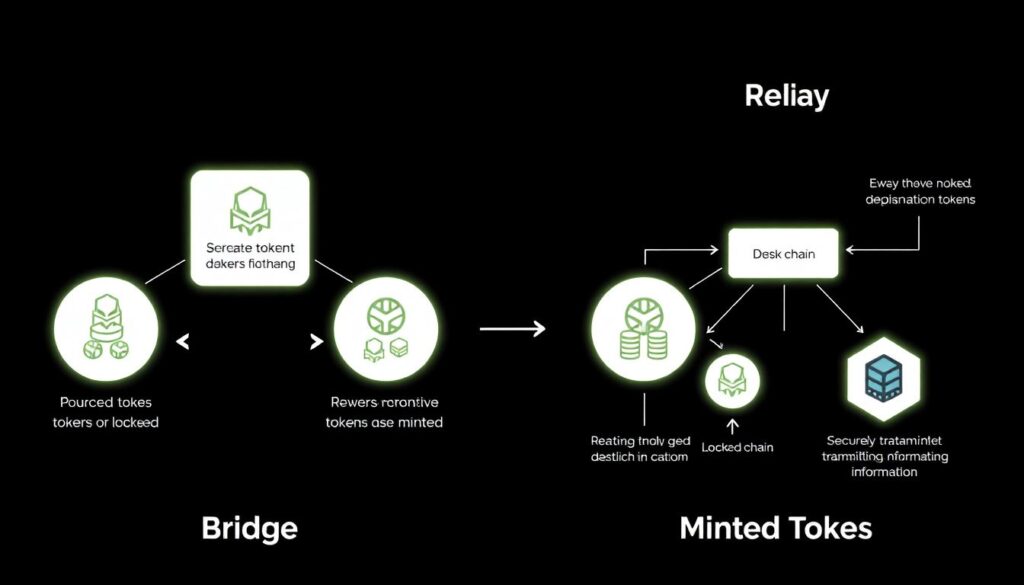
Before touching any code or wallets, it helps to decode the jargon. A “bridge” is a mechanism that lets you move tokens or information from one chain to another, usually by locking assets on the source chain and minting a representation on the destination. A “relay” is more like a blockchain interpreter that reads events from one network and proves them on another. Finally, “cross‑chain messaging” moves not money, but instructions: for example, “execute this trade on chain B when something happens on chain A”.
What tools you actually need
To experiment safely, you don’t need a trading desk or a PhD. Start with a browser and a multi chain wallet with blockchain interoperability support, such as a wallet that can connect to Ethereum, Polygon, and other EVM chains. Add a block explorer for each network, plus access to testnets where you can play with fake coins. If you plan to go deeper, install a code editor and Node.js so you can call interoperability smart contracts. For serious teams, expert‑audited SDKs and dashboards are strongly recommended by security researchers.
– Browser wallet (multi‑chain)
– Access to testnets and faucets
– Block explorers for all target networks
Step‑by‑step: your first cross‑chain transfer
A practical way to “feel” interoperability is to try a small transfer on a well‑known bridge. First, pick one of the best cross chain bridges for crypto investors that clearly explains fees and risks; reputable researchers advise avoiding unknown bridges with tiny TVL. Second, connect your wallet on the source chain and choose a modest amount. Third, confirm the transaction and patiently wait for finality and verification on the destination chain. Finally, check a block explorer and your wallet balance; if everything matches, you’ve just completed a cross‑chain move.
How bridges and protocols work under the hood
Most beginner‑friendly bridges use a lock‑and‑mint model: your tokens are locked in a smart contract or custodian on chain A, while new “wrapped” tokens are minted on chain B. More advanced interoperability protocols use light client proofs or shared security, where chains verify each other cryptographically instead of trusting a centralized multisig. When experts compare blockchain interoperability solutions for defi projects, they focus on how these proofs are generated, who can operate the relayers, and how the system behaves if one component fails or goes offline.
Interoperability for DeFi and everyday users
From a DeFi user’s perspective, interoperability unlocks better yields and liquidity. Instead of being stuck on one network, you can deposit on a lending protocol on chain A, then route profits through a DEX on chain B, while an interoperable protocol syncs your positions. Security auditors repeatedly warn beginners: never chase APY blindly across chains. Start small, read audit reports, and favor protocols that clearly document their cross‑chain risk model and insurance mechanisms, rather than hiding complexity behind glossy dashboards and buzzwords.
Enterprises and professional integration

On the corporate side, interoperability is less about yield and more about compliance, data sharing, and system design. Companies look at enterprise blockchain integration and interoperability services that can connect private ledgers with public chains without leaking sensitive information. Modern blockchain interoperability platforms for enterprises may offer permissioned relays, granular access control, and detailed logging for regulators. Architects advise piloting with non‑critical data first, establishing clear rollback procedures, and building threat models that include not only hackers, but also misconfigured internal systems.
Recommended practices from experts
Researchers and veteran engineers converge on a few simple rules. Treat every bridge as a high‑value target and assume it can fail. Avoid keeping your entire portfolio on one protocol; distribute funds across several audited options. When picking tooling, prioritize open‑source stacks and public bug bounty programs. For teams, experts recommend formalizing incident response: who pauses contracts, who talks to users, how monitoring alerts are handled. These practices sound corporate, but even small DeFi teams benefit from writing them down early.
– Favor audited, open‑source protocols
– Diversify bridges and chains you rely on
– Document incident and rollback procedures
Typical problems and basic troubleshooting
Sooner or later, something will go odd: a transfer stuck in “pending”, a UI glitch, or a missing token display. First, don’t panic or spam more transactions; check official status pages and explorers to see whether the transaction actually finalized. If tokens arrived but your wallet doesn’t show them, manually add the token contract from a trusted source. For persistent issues, join official Discord or Telegram channels instead of random forums; support teams behind blockchain interoperability solutions for defi projects often track specific outages in real time.
How to keep learning and avoid common traps

Interoperability moves fast, so yesterday’s “safest bridge” can become tomorrow’s exploit headline. Build habits rather than memorizing brand names: verify contract addresses, start on testnets, read security postmortems, and follow independent researchers on X and GitHub. As you grow more confident, you can explore SDKs, relayer code, and more advanced enterprise blockchain integration and interoperability services. The goal isn’t to master every protocol, but to understand the core patterns well enough to judge new interoperability narratives without falling for pure hype.