Understanding the Importance of Transaction Timing in Trading
Precision and timing have always played a pivotal role in financial markets. In the realm of trading, even milliseconds can define the line between profit and loss. Transaction timing refers to the strategic moment when a buy or sell order is executed. Optimizing this timing can significantly enhance a trader’s profitability by minimizing slippage, maximizing price efficiency, and aligning with market momentum. Whether operating in high-frequency environments or swing trading over days, understanding when to enter and exit positions is critical. This article will explore effective tools, a phased optimization strategy, and real-world cases to bridge the gap between theory and success.
Essential Tools for Timing Optimization
Market Data Feeds and Latency Monitoring
At the core of precise transaction timing lies access to real-time market data. Traders require low-latency data feeds that offer up-to-the-millisecond price updates. Platforms such as Bloomberg Terminal or Thomson Reuters Eikon provide institutional-grade analytics, while APIs from exchanges deliver raw tick data crucial for algorithmic setups. Accompanying this, latency monitoring software helps detect delays in order routing, allowing traders to identify and eliminate bottlenecks in their infrastructure.
Advanced Order Types and Trading Algorithms
Beyond simple market or limit orders, traders can leverage advanced order types like iceberg, TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price), and VWAP (Volume-Weighted Average Price) to optimize execution timing. Algorithmic strategies built on Python, C++, or Java can automate decision trees that account for volatility, news releases, or order book depth. These tools reduce emotional bias and execute trades at ideal moments based on pre-defined logic.
Economic Calendars and News Aggregators
Timing trades around macroeconomic events demands awareness of when key data will be released. Economic calendars from Investing.com or Forex Factory highlight announcements like interest rate decisions, employment numbers, and GDP reports. Coupled with news aggregators such as Benzinga Pro, traders can react instantly to sentiment shifts that influence short-term price movements.
Step-by-Step Guide to Optimizing Timing
Step 1: Analyze Historical Volatility Patterns
The first step involves understanding the typical behavior of your chosen asset across different time frames. Use historical data to identify when the asset exhibits peak volatility—commonly around market open, macroeconomic announcements, or earnings reports. This insight helps in predicting periods of greater price movement, offering better risk–reward opportunities.
Step 2: Determine Optimal Trade Windows
After identifying periods of high volatility, narrow down optimal trade windows. For example, in U.S. equities, a large portion of intraday movement happens between 9:30 and 11:00 AM EST. Forex traders often find the London–New York overlap (8:00–12:00 EST) to be rich in liquidity and volatility. Deploying trades within these windows can improve fill quality and reduce slippage.
Step 3: Incorporate Technical and Sentiment Indicators
Employ indicators like Relative Strength Index (RSI), Bollinger Bands, and Moving Averages to confirm timing. Combine them with real-time sentiment data from sources like Twitter feeds or Reddit forums. For instance, a rising RSI during a positive earnings surprise may indicate a strong short-term entry point, while extreme social media euphoria might signal an overheated market ripe for a correction.
Step 4: Simulate and Backtest Strategies
Before going live, use simulation tools such as MetaTrader’s Strategy Tester or TradingView’s Pine Script environment to backtest your timing strategy. Analyze how different entry and exit times influence overall returns. Focus not just on profit but also on drawdowns, maximum adverse excursions, and recovery factors. The goal is to validate that your timing logic is statistically significant.
Step 5: Automate and Monitor Execution
Once validated, automate execution through a trading bot or platform with programmable logic. Ensure you have real-time monitoring in place to track performance, latency, and errors. For example, if your bot consistently executes trades milliseconds after ideal windows, it may require server-side adjustments or a closer server location to the exchange.
Troubleshooting Common Timing Issues
Slippage and Order Execution Delays
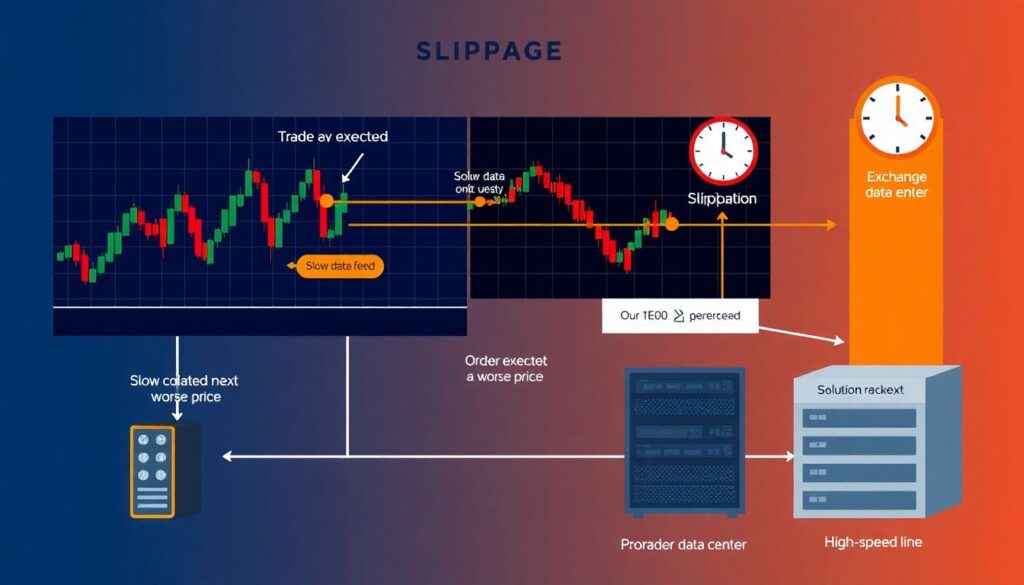
One of the most common issues in timing optimization is slippage—when the order is filled at a worse price than expected. This often results from slow data feeds or order routing delays. To mitigate this, consider colocating your trading server near exchange data centers and using Direct Market Access (DMA) platforms, which bypass intermediaries and reduce latency.
Misinterpreting Market Signals
Automated systems can misfire if they rely on flawed assumptions. For example, a strategy that buys every time RSI drops below 30 may perform poorly in trending markets. Regularly update your indicators and validate their predictive power using walk-forward analysis. Avoid overfitting by limiting the number of parameters and testing across multiple market conditions.
Overtrading During Low-Liquidity Periods
Not all market hours offer equal opportunity. Executing trades during low-volume periods, like after-hours sessions or holidays, can lead to poor fills and increased spreads. Restrict your strategy to periods verified for liquidity and price efficiency. Use volume thresholds or average true range (ATR) filters to avoid suboptimal execution.
Real-World Case Studies
Case 1: High-Frequency Crypto Trading

In 2022, a proprietary crypto trading firm implemented latency-sensitive bots across multiple exchanges. They discovered that executing trades even 50ms faster than competitors yielded a 0.3% gain per transaction due to price arbitrage. By colocating servers and optimizing their codebase for efficiency, they improved annual returns by over 25%.
Case 2: Swing Trading Around Earnings
A retail trader specializing in tech stocks backtested hundreds of earnings dates and found that stocks beating expectations with >5% surprise often surged within the first 15 minutes after market open. By setting limit buy orders pre-market and exiting within 1 hour post-open, they achieved a 65% win rate and average return of 3.8% per trade across a 12-month period.
Case 3: Forex Scalping During London–US Overlap
A forex trader focused on EUR/USD implemented a scalping strategy that only entered when spreads were below 0.3 pips and volume exceeded 80% of average hourly levels. By restricting trades to 8:00–11:00 EST and integrating economic news filters, the trader reduced drawdowns by 40% and improved consistency.
Final Thoughts
Optimizing transaction timing is not about predicting the future, but about positioning yourself where probability favors your outcome. With the right tools, analytical rigor, and constant performance evaluation, traders can fine-tune execution to gain a decisive edge. While markets will always retain an element of uncertainty, timing optimization turns randomness into opportunity.

